Spotting a random bump around your genital area is enough to signal many people’s alarms ringing. This panic is, of course, justified considering how sensitive the genital area is. Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) seem to cross new highs each year, breaking their previous records.
So, rationally if you notice a bump in that area, you might be anxious to rule out any bad news. However, your spot may have an explanation as simple as ingrown hair. Although ingrown hairs can also get infected, they are non-contiguous, significantly reducing their potential for harm.
Although some ingrown hair bumps are pretty similar to herpes sores, close observation can help you correctly identify which one of these conditions is afflicting you.
To differentiate the two similar-looking skin conditions, let’s look at what each of these conditions is and what symptoms it is accompanied by.
What Is Herpes?

Herpes is the name given to the skin infection or the nervous system caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV).
Types of Herpes
Herpes causes sores to erupt on the skin but according to location, there are two types of this skin disease.
- Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1): It is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact.
- Herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2): It is the culprit behind occurrences of genital herpes. In genital herpes, sores appear around the genitals or the rectum. Genital herpes is transmittable through sexual contact, which may be skin-to-skin contact or contact with sexual fluids. The findings of the World Health Organization show that 49.5 million people across the globe in the age range of 15-49 years suffer from HSV-2 infection.
The thing about genital herpes is that there is no cure, just management of symptoms of the disease. Additionally, the virus stays in your body once you’re infected, causing reinfections. The virus can be passed whether the infection is symptomatic or asymptomatic.
Symptoms of Genital Herpes
The following symptoms indicate the onset of the genital herpes infection:
- The first thing that happens after the infection sets in is the occurrence of flu-like symptoms. These symptoms include fever, chills, headaches, body and muscle aches, and fatigue.
- Your lymph nodes, present around the pelvic area, in your throat, and in your armpits, may display swelling signs.
- A tingling or burning sensation might be felt around the genitals before visible symptoms. Itching may also be experienced.
- The skin around the genitals may appear to be raw, red, and cracked.
- A patch might develop on the skin around the genitals. Small blisters soon erupt around the genitals, anus, thighs, and buttocks.
- The blisters burst to become open sores that ooze fluid and may bleed. The sores usually crust over within a week and scab over in about four weeks.
- Women may experience different symptoms, including cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix), unusual vaginal discharge, burning sensation while peeing, and urinary retention due to the urethra being blocked by the swelling.
What Is Ingrown Hair?

Ingrown hairs occur when the growing end of your hair shaft curls downwards and grows into the hair follicle instead of breaking through the epidermis. The cause and treatment of ingrown hair are much like what occurs in pili multigemini, a condition in which multiple hairs begin to grow out of a single follicle.
This condition is more common among people with curly, thick, or coarse hair. People who shave or tweeze body hair tend to have a higher risk of having ingrown hairs. Since many people shave, wax, or tweeze their genital region often, there is a possibility of ingrown hairs occurring in the genital area.
Although ingrown hairs are usually not a severe cause for concern, they can cause painful, red bumps that may inflate and turn into cysts that leave scarring.
Symptoms of Ingrown Hair
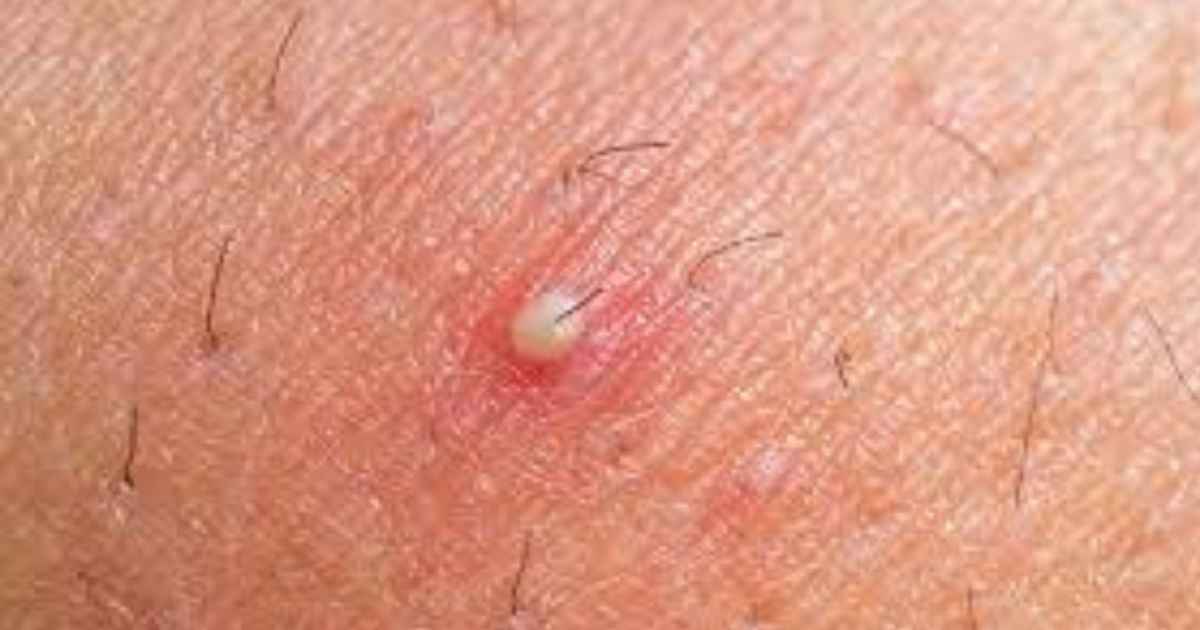
The following are the symptoms of ingrown hair:
- The skin may appear irritated and itchy, with a rash appearing.
- The ingrown hair blocks the hair follicle, causing the area to become inflamed. This results in a single pimple-like raised bump on the skin. The bump may be red, yellowish, or brown in color.
- The bump might be tender and painful to the touch.
- If the pimple is accidentally popped or grows into a cyst, it might get infected and become a sore. This condition is known as folliculitis.
Differences: Is It An Ingrown Hair Or Herpes?

Folliculitis sores are easy to mistake as herpes sores to an untrained eye.
Let us look at the differences between the two conditions that can help determine the nature of the sores around the genital region.
1. The Appearance of The Bump Or Sore
- Herpes sores are raised above the skin. They have a blister-like, water-filled appearance. On the other hand, the bump is below the skin with ingrown hairs.
- Herpes sores appear in clusters, while ingrown hairs give rise to isolated, red, yellow, or brown, pimple-like bumps.
- If ruptured, herpes sores ooze a yellow discharge, whereas infected ingrown hairs release a white-colored discharge.
- Another thing you might notice is a thin line, barely visible inside the sore. If you see such a line, your sore is most certainly an ingrown hair, with the visible line being the hair that is growing into the follicle.
- Genital herpes blisters can last 2-4 weeks and develop into ulcers within 2-12 days of the onset of the rash. Ingrown hair bumps usually resolve within a week.
2. Location of The Bump
If your bump is around your rectal area, it is likely to be genital herpes as ingrown hairs appear in areas of hair growth, especially curly and coarse hair like in the pubic region.
Even for bumps in the genital region, genital herpes is more likely to occur closer to the genitals.
If your sores only appear on one side of your genitals, you probably have genital herpes.
3. Pain Level of The Bump
Ingrown hair only causes mild pain and tenderness, whereas genital herpes causes an excruciating burning sensation.
4. Circumstances Before Appearance of Bumps
- If your bumps occur one to two days after taking a hair removal treatment for your genital region, like waxing, tweezing, or shaving, they are likely to be caused by ingrown hairs.
- If you suffered from tingling or burning in the genital area, developed flu-like symptoms, and had swollen lymph nodes before the appearance of bumps, you probably have genital herpes.
- If you feel a burning sensation while urinating due to urine passing over the sores, the sores are probably caused by genital herpes.
5. Frequency of Outbreaks
Ingrown hairs happen after you take any hair removal treatments.
Genital herpes reinfections frequently occur in the first few years after you first contract the virus before settling into a cycle of about two outbreaks annually.
Conclusion
It is good to be vigilant about any strange bumps in your genital area. A quick assessment of your bump’s appearance and a recall of any symptoms you may have had previously can help stave off the panic that may arise.
However, since genital herpes is a contagious disease, any signs pointing to it should lead you to your doctor’s office to get a proper diagnosis.

A fervent champion for holistic well-being, graces this community with her expertise in health and fitness. With a solid educational foundation in physical fitness and a commitment to empowering others, Sara distills her extensive knowledge and experience into actionable insights. Her writing, firmly grounded in evidence-based practices, aims to demystify health complexities and inspire readers to cultivate sustainable habits for a balanced life. As a certified fitness trainer, Sara offers a well-rounded perspective on wellness. Join Sara on this transformative journey towards a happier, healthier, and more vibrant you.






Loading…